IMF’s recent engagements on infrastructure governance
| Public Investment Management Assessment (PIMA) | April 2017 |
| PIMA Follow-up: Strengthening Oversight over Public Corporations, Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) and Fiscal Risks | May 2020 |
| PPP Fiscal Risk Management Workshop | May 2023 |
| Climate PIMA (C-PIMA) | July 2023 |
| PPP Fiscal Risk Assessment Model (PFRAM) Training | September 2023 |
Summary of PIMA report
(Published in December 2017)
Jordan’s public finances have deteriorated since the mid-2000s, resulting in a significant reduction in public investment. In response to several negative external shocks, notably the Iraq and Syria crises and the 2008 global financial crisis, the government has reduced public investment and stepped up the use of public-private partnerships (PPPs). Capital expenditure as a share of total expenditure for the general government decreased from around 7 percent of GDP in the early 2000s to around 4 percent of GDP in the years following the 2008 global financial crisis. Consequently, Jordan’s public capital stock stood at 77 percent of GDP in 2015, compared to 140 percent of GDP in 1990, and the capital stock per capita in 2015 was lower than those of peer countries with similar income levels..
⚠ Some users may experience reduced functionality using Internet Explorer. For the optimal experience, use Chrome or another alternative browser.
- Chart View: Institutional Design vs. Effectiveness
- Chart View: Comparison with Peers
- Learn how to interpret the flower chart
PHASES
Planning (Institutions 1-5) Allocation (Institutions 6-10) Implementation (Institutions 11-15)
Loading...
INSTITUTION
1. Fiscal Targets and Rules
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
1.a. Is there a target or limit for government to ensure debt sustainability?
Loading...
1.b. Is fiscal policy guided by one or more permanent fiscal rules?
Loading...
1.c. Is there a medium-term fiscal framework (MTFF) to align budget preparation with fiscal policy?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
2. National and Sectoral Planning
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
2.a. Does the government prepare national and sectoral strategies for public investment?
Loading...
2.b. Are the government’s national and sectoral strategies or plans for public investment costed?
Loading...
2.c. Do sector strategies include measurable targets for the outputs and outcomes of investment projects?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
3. Coordinating Between Entities
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
3.a. Is capital spending by SNGs, coordinated with the central government?
Loading...
3.b. Does the central government have a transparent, rule-based system for making capital transfers to SNGs, and for providing timely information on such transfers?
Loading...
3.c. Are contingent liabilities arising from capital projects of SNGs, PCs, and PPPs reported to the central government?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
4. Project Appraisal
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
4.a. Are major capital projects subject to rigorous technical, economic, and financial analysis?
Loading...
4.b. Is there a standard methodology and central support for the appraisal of projects?
Loading...
4.c. Are risks taken into account in conducting project appraisals?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
5. Alternative Infrastructure Financing
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
5.a. Does the regulatory framework support competition in contestable markets for economic infrastructure (e.g., power, water, telecoms, and transport)?
Loading...
5.b. Has the government published a strategy/policy for PPPs, and a legal/regulatory framework which guides the preparation, selection, and management of PPP projects?
Loading...
5.c. Does the government oversee the investment plans of public corporations (PCs) and monitor their financial performance?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
6. Multiyear Budgeting
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
6.a. Is capital spending by ministry or sector forecasted over a multiyear horizon?
Loading...
6.b. Are there multiyear ceilings on capital expenditure by ministry, sector, or program?
Loading...
6.c. Are projections of the total construction cost of major capital projects published?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
7. Budget Comprehensiveness and Unity
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
7.a. Is capital spending mostly undertaken through the budget?
Loading...
7.b. Are all capital projects, regardless of financing source, shown in the budget documentation?
Loading...
7.c. Are capital and recurrent budgets prepared and presented together in the budget?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
8. Budgeting for Investment
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
8.a. Are total project outlays appropriated by the legislature at the time of a project’s commencement?
Loading...
8.b. Are in-year transfers of appropriations (virement) from capital to current spending prevented?
Loading...
8.c. Is the completion of ongoing projects given priority over starting new projects?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
9. Maintenance and Funding
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
9.a. Is there a standard methodology for estimating routine maintenance needs and budget funding?
Loading...
9.b. Is there a standard methodology for determining major improvements (e.g. renovations, reconstructions, enlargements) to existing assets, and are they included in national and sectoral investment plans?
Loading...
9.c. Can expenditures relating to routine maintenance and major improvements be identified in the budget?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
10. Project Selection
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
10.a. Does the government undertake a central review of major project appraisals before decisions are taken to include projects in the budget?
Loading...
10.b. Does the government publish and adhere to standard criteria, and stipulate a required process for project selection?
Loading...
10.c. Does the government maintain a pipeline of appraised investment projects for inclusion in the annual budget?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
11. Procurement
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
11.a. Is the procurement process for major capital projects open and transparent?
Loading...
11.b. Is there a system in place to ensure that procurement is monitored adequately?
Loading...
11.c. Are procurement complaints review process conducted in a fair and timely manner?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
12. Availability of Funding
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
12.a. Are ministries/agencies able to plan and commit expenditure on capital projects in advance on the basis of reliable cash-flow forecasts?
Loading...
12.b. Is cash for project outlays released in a timely manner?
Loading...
12.c. Is external (donor) funding of capital projects fully integrated into the main government bank account structure?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
13. Portfolio Management and Oversight
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
13.a. Are major capital projects subject to monitoring during project implementation?
Loading...
13.b. Can funds be re-allocated between investment projects during implementation?
Loading...
13.c. Does the government adjust project implementation policies and procedures by systematically conducting ex post reviews of projects that have completed their construction phase?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
14. Management Project Implementation
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
14.a. Do ministries/agencies have effective project management arrangements in place?
Loading...
14.b. Has the government issued rules, procedures and guidelines for project adjustments that are applied systematically across all major projects?
Loading...
14.c. Are ex post audits of capital projects routinely undertaken?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
15. Monitoring of Public Assets
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
15.a. Are asset registers updated by surveys of the stocks, values, and conditions of public assets regularly?
Loading...
15.b. Are nonfinancial asset values recorded in the government financial accounts?
Loading...
15.c. Is the depreciation of fixed assets captured in the government’s operating statements?
Loading...
PIMA SCORES
Income Groups
Regions
PHASES
Planning (Institutions 1-5) Allocation (Institutions 6-10) Implementation (Institutions 11-15)
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Loading...
Sources: IMF Investment and Capital Stock Dataset, 2021; and IMF staff calculations based on PIMA reports. Note: The data displayed above might differ from the data in the PIMA report as the latter might incorporate additional information obtained during the PIMA mission.
INSTITUTION
1. Fiscal Targets and Rules
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
1.a. Is there a target or limit for government to ensure debt sustainability?
Loading...
1.b. Is fiscal policy guided by one or more permanent fiscal rules?
Loading...
1.c. Is there a medium-term fiscal framework (MTFF) to align budget preparation with fiscal policy?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
2. National and Sectoral Planning
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
2.a. Does the government prepare national and sectoral strategies for public investment?
Loading...
2.b. Are the government’s national and sectoral strategies or plans for public investment costed?
Loading...
2.c. Do sector strategies include measurable targets for the outputs and outcomes of investment projects?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
3. Coordinating Between Entities
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
3.a. Is capital spending by SNGs, coordinated with the central government?
Loading...
3.b. Does the central government have a transparent, rule-based system for making capital transfers to SNGs, and for providing timely information on such transfers?
Loading...
3.c. Are contingent liabilities arising from capital projects of SNGs, PCs, and PPPs reported to the central government?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
4. Project Appraisal
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
4.a. Are major capital projects subject to rigorous technical, economic, and financial analysis?
Loading...
4.b. Is there a standard methodology and central support for the appraisal of projects?
Loading...
4.c. Are risks taken into account in conducting project appraisals?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
5. Alternative Infrastructure Financing
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
5.a. Does the regulatory framework support competition in contestable markets for economic infrastructure (e.g., power, water, telecoms, and transport)?
Loading...
5.b. Has the government published a strategy/policy for PPPs, and a legal/regulatory framework which guides the preparation, selection, and management of PPP projects?
Loading...
5.c. Does the government oversee the investment plans of public corporations (PCs) and monitor their financial performance?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
6. Multiyear Budgeting
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
6.a. Is capital spending by ministry or sector forecasted over a multiyear horizon?
Loading...
6.b. Are there multiyear ceilings on capital expenditure by ministry, sector, or program?
Loading...
6.c. Are projections of the total construction cost of major capital projects published?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
7. Budget Comprehensiveness and Unity
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
7.a. Is capital spending mostly undertaken through the budget?
Loading...
7.b. Are all capital projects, regardless of financing source, shown in the budget documentation?
Loading...
7.c. Are capital and recurrent budgets prepared and presented together in the budget?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
8. Budgeting for Investment
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
8.a. Are total project outlays appropriated by the legislature at the time of a project’s commencement?
Loading...
8.b. Are in-year transfers of appropriations (virement) from capital to current spending prevented?
Loading...
8.c. Is the completion of ongoing projects given priority over starting new projects?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
9. Maintenance and Funding
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
9.a. Is there a standard methodology for estimating routine maintenance needs and budget funding?
Loading...
9.b. Is there a standard methodology for determining major improvements (e.g. renovations, reconstructions, enlargements) to existing assets, and are they included in national and sectoral investment plans?
Loading...
9.c. Can expenditures relating to routine maintenance and major improvements be identified in the budget?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
10. Project Selection
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
10.a. Does the government undertake a central review of major project appraisals before decisions are taken to include projects in the budget?
Loading...
10.b. Does the government publish and adhere to standard criteria, and stipulate a required process for project selection?
Loading...
10.c. Does the government maintain a pipeline of appraised investment projects for inclusion in the annual budget?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
11. Procurement
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
11.a. Is the procurement process for major capital projects open and transparent?
Loading...
11.b. Is there a system in place to ensure that procurement is monitored adequately?
Loading...
11.c. Are procurement complaints review process conducted in a fair and timely manner?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
12. Availability of Funding
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
12.a. Are ministries/agencies able to plan and commit expenditure on capital projects in advance on the basis of reliable cash-flow forecasts?
Loading...
12.b. Is cash for project outlays released in a timely manner?
Loading...
12.c. Is external (donor) funding of capital projects fully integrated into the main government bank account structure?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
13. Portfolio Management and Oversight
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
13.a. Are major capital projects subject to monitoring during project implementation?
Loading...
13.b. Can funds be re-allocated between investment projects during implementation?
Loading...
13.c. Does the government adjust project implementation policies and procedures by systematically conducting ex post reviews of projects that have completed their construction phase?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
14. Management Project Implementation
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
14.a. Do ministries/agencies have effective project management arrangements in place?
Loading...
14.b. Has the government issued rules, procedures and guidelines for project adjustments that are applied systematically across all major projects?
Loading...
14.c. Are ex post audits of capital projects routinely undertaken?
Loading...
INSTITUTION
15. Monitoring of Public Assets
SUMMARY ASSESSMENT
Institutional Design: ---
Effectiveness: ---
OVERALL SCORES
Loading...
15.a. Are asset registers updated by surveys of the stocks, values, and conditions of public assets regularly?
Loading...
15.b. Are nonfinancial asset values recorded in the government financial accounts?
Loading...
15.c. Is the depreciation of fixed assets captured in the government’s operating statements?
Loading...
How To Read The Flower Chart
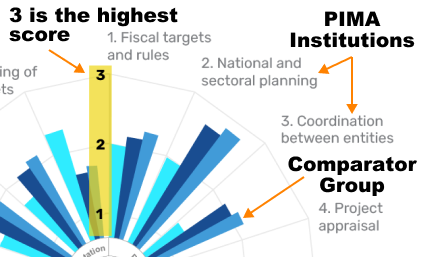 |
Scoring Each institution is analyzed along three dimensions that reflect the key features of the given institution, resulting in a total of 45 dimensions. Three possible scores are assigned to each dimension (1: not met, 2: partially met, 3: fully met) and their average within an institution produces a score for that institution. PIMA scores are summarized in a chart that allows comparison with its comparators. In the chart, the further the away from the center, the higher the PIMA scores.
|
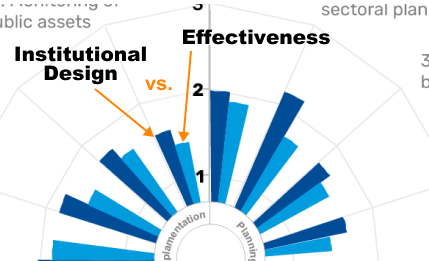 |
Institutional Design and Effectiveness Another key feature of the PIMA is that it assesses both institutional design (“what is on paper”) and effectiveness (“what is in practice”) of a given country, because there is often a gap between the design of formal rules and how they are implemented in practice, due to capacity constraints among others. |
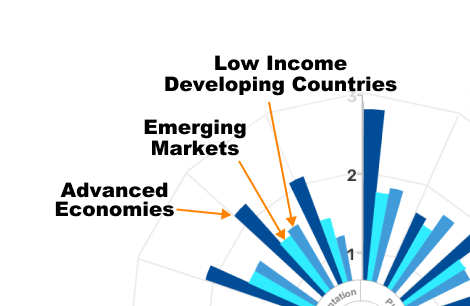 |
Scores by Income Level All countries, most notably emerging markets and low-income developing countries, have significant room to improve their infrastructure governance to increase effectiveness in public investment.
|
What Countries are in Each Income Group
The countries listed below cover only refer to those that have conducted PIMA.
Advanced economies (ADV) and low-income developing countries (LIDC) are classified according to latest World Economic Outlook. Emerging market (EME) include those not classified as advanced economies or low-income developing countries. Fragile states are classified based on IMF Policy Paper, Macroeconomic Developments and Prospects in Low-Income Developing Countries, 2018.
Advanced Economies (ADV)
Estonia Ireland Poland Slovak Republic United Kingdom |
Emerging Markets (EME)
Albania Angola Anguilla Argentina Armenia Belize Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil Bulgaria |
Costa Rica Croatia Egypt El Salvador Eswatini Gabon Georgia Grenada Guyana Indonesia |
Jordan Kosovo Lebanon Malaysia Maldives Mauritius Mexico Montenegro Morocco North Macedonia |
Peru Philippines Romania Serbia Sri Lanka Thailand Timor-Leste Tunisia Ukraine |
Low-Income Developing Countries (LIDC)
Bangladesh Benin Burkina Faso Cambodia Cameroon Côte d'Ivoire Democratic Republic of Congo The Gambia Ghana |
Guinea Haiti Honduras Kenya Kiribati Kyrgyz Republic Liberia Madagascar Malawi |
Mali Mauritania Moldova Mongolia Mozambique Nepal Niger Nigeria Rwanda |
Senegal Sierra Leone Togo Uzbekistan Vietnam Zambia |
Fragile States (FS)
Côte d'Ivoire Democratic Republic of Congo Gambia Guinea Haiti Kiribati |
Kosovo Lebanon Liberia Madagascar Malawi Maldives |
Mali Sierra Leone Timor-Leste Togo |